-
×
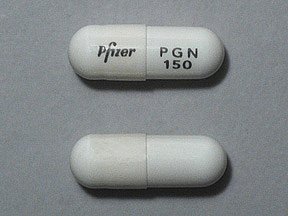 Lyrica (Pregabalin) 150mg capsule
1 × $2.50
Lyrica (Pregabalin) 150mg capsule
1 × $2.50 -
×
 Androlic (Oxymetholone) 50mg
1 × $1.10
Androlic (Oxymetholone) 50mg
1 × $1.10 -
×
 Anavar (Oxandrolone) 10mg
1 × $0.90
Anavar (Oxandrolone) 10mg
1 × $0.90 -
×
 Ativan (Lorazepam) 1mg
1 × $3.00
Ativan (Lorazepam) 1mg
1 × $3.00 -
×
 Avinza (Morphine Sulfate) 120mg capsule
1 × $4.50
Avinza (Morphine Sulfate) 120mg capsule
1 × $4.50
Subtotal: $12.00